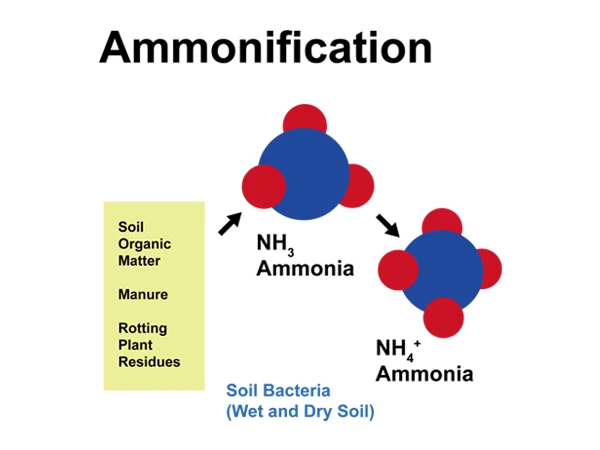
Ammonification Process

The AAO (Anaerobic-Anoxic-Oxic) process is an advanced biological treatment technology widely used in wastewater treatment plants, primarily for removing organic matter and nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus from wastewater. The treatment efficiency generally reaches: BOD5 and SS at 90%–95%, total nitrogen above 70%, and phosphorus around 90%.
First, the wastewater enters the anaerobic zone from the primary sedimentation tank, where it fully mixes with the return sludge. After a certain period (1–2 h) of anaerobic decomposition, part of the BOD is removed. Through the denitrification process, some nitrogen-containing compounds are converted into N2 and released. Phosphate-accumulating microorganisms (like phosphate-accumulating organisms) in the return sludge release phosphorus to meet the bacteria's phosphorus requirements.
Then the wastewater flows into the anoxic tank, where denitrifying bacteria use the undecomposed carbon-containing organic matter in the wastewater as a carbon source to reduce NO2- and NO3-, which are returned from the aerobic tank through internal circulation, to N2 and release it.
Next, the wastewater flows into the aerobic tank, where NH4-N in the water undergoes nitrification to form nitrite and nitrate. Meanwhile, the organic matter in the water is oxidized and decomposed to provide energy for phosphorus-accumulating microorganisms. These microorganisms absorb phosphorus from the water, which enters their cellular structure and accumulates within them. After sedimentation and separation, the phosphorus-rich sludge is discharged from the system.
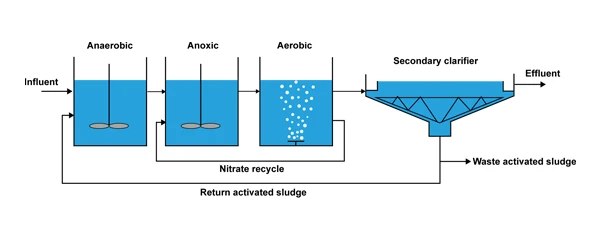
The overall AAO process includes four parts: primary pretreatment, secondary biological treatment, tertiary advanced treatment, and sludge treatment. The specific structures are as follows:
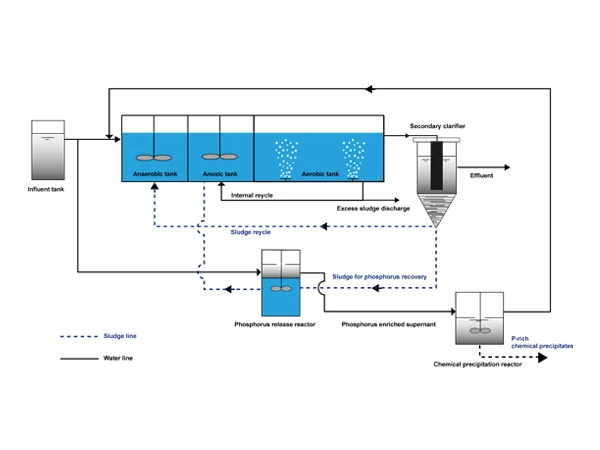
The AAO process is a biological treatment method commonly used in wastewater treatment, primarily for the simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from water.
Denitrification:
Biological nitrogen removal refers to the process where organic nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen in wastewater are converted into nitrogen gas through ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification under the combined action of microorganisms.

Ammonification Process
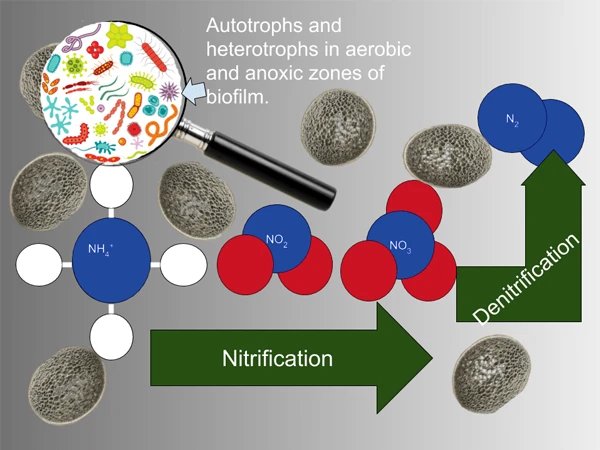
Nitrification & Denitrification Process
Principle of Phosphorus Removal
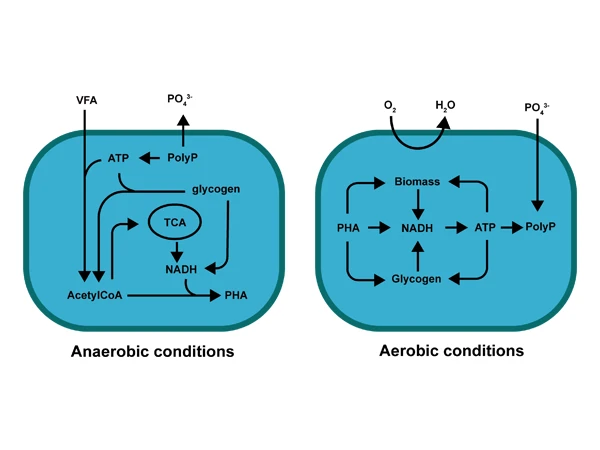
Biological phosphorus removal utilizes phosphate-accumulating organisms (PAOs) that release phosphorus under anaerobic conditions and absorb phosphorus in excess of their physiological needs under aerobic conditions. The phosphorus is stored in the cells in a polymeric form, forming high-phosphorus sludge, which is then removed from the system, achieving phosphorus removal from wastewater.
Return sludge is a type of activated sludge that is separated from the secondary sedimentation (or sedimentation zone) and returned to the anaerobic tank.
In a normal biochemical system, it is essential to ensure the stability of the sludge volume to maintain the normal operation of the system. The reproduction rate of bacteria in the system is much lower than the amount of wastewater removed, so to ensure the stability of the biochemical system, sludge must be returned.
To determine the amount of return sludge, the sludge recycle ratio must first be determined. The sludge recycle ratio is the ratio of the return sludge flow rate in the sludge tank to the influent flow rate. There are two methods to calculate it, as shown below:
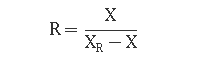
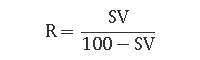
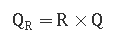
For example, if the wastewater flow rate is 300 m3/h and the sludge recycle ratio is calculated to be 70%, then the return sludge volume is: 300×70%=210m 3/h
Nitrate recycle refers to the process of returning the mixed liquor from the aerobic tank to the anoxic tank to increase the concentration of nitrate nitrogen in the anoxic tank, thereby promoting the denitrification reaction. It has little relation to phosphorus removal.
The nitrate recycle ratio refers to the ratio of the mixed liquor recycle flow rate to the influent flow rate, usually denoted as r. The nitrate recycle ratio r directly determines the denitrification efficiency. For a given biological nitrogen removal system, there exists an optimal internal recycle ratio at which the denitrification efficiency is maximized.
Assuming the biological nitrification efficiency and denitrification efficiency are 100%, meaning all TKN is nitrified into nitrate nitrogen, and all nitrate nitrogen recycled to the anoxic zone is denitrified to N2, the denitrification efficiency EDN at this point is:
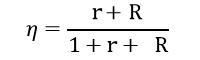
For example: If the sludge recycle ratio is 70% and the nitrate recycle ratio is 400%, then the ammonia removal efficiency is: (400%+70%)(1+400%+70%)=82.5%
The AAO process is a flexible operation that can focus on denitrification removal, or phosphorus removal, or both. If both denitrification and phosphorus removal are required, F/M is generally controlled at 0.1–0.18k BOD5 /(kg MLVSS•d), and SRT should generally be controlled at 8–15 days.
Hydraulic retention time is related to factors such as influent concentration and temperature. The HRT in the anaerobic zone is generally 1–2 hours; the HRT in the anoxic zone is 1.5–2 hours; the HRT in the aerobic zone should generally be 6 hours. Excessive or insufficient hydraulic retention time will affect the process.
The internal recycle ratio r is generally 200%–500%, depending on the influent TKN concentration and the required denitrification efficiency. The external recycle ratio R is generally in the range of 50%–100%. To ensure that denitrification and secondary phosphorus release do not occur in the secondary sedimentation tank, R should be minimized to avoid bringing too much NO₃-N back to the anaerobic zone, which would interfere with phosphorus release and reduce phosphorus removal efficiency.
DO in the anaerobic zone should be controlled below 0.2 mg/L, in the anoxic zone below 0.5 mg/L, and in the aerobic zone 2–3 mg/L.
For biological nitrogen removal, COD/TKN should be greater than 4.0, while biological phosphorus removal requires COD/TP greater than 20. If the COD/TKN value is low, methanol should be added as a nutrient source; if the COD/TP value is low, acetic acid or other lower fatty acids should be added.
In the AAO biological phosphorus and nitrogen removal system, the pH of the sludge mixed liquor should be controlled above 7.0. If the pH is less than 6.5, alkalinity can be increased.
The higher the temperature, the more favorable it is for biological nitrogen removal. When the temperature is below 15 °C, the efficiency of biological nitrogen removal will significantly decrease. Conversely, lower temperatures are beneficial for phosphorus removal.
When certain heavy metal ions, complex anions, and some organic matter enter the water treatment system, if they exceed a certain concentration, they can cause activated sludge toxicity, inhibiting the activity of certain microorganisms.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
To make the water treatment system have high denitrification efficiency, significant energy-saving and consumption-reducing effects, stronger shock load resistance, and lower sludge yield, the traditional AAO process is improved. The common improvement methods are as follows:
Aerobic and anoxic double internal recycling process