Anaerobic biofilm formation

The MBBR process is a wastewater treatment technology that combines the advantages of traditional fluidized bed and biological contact oxidation methods, providing excellent nitrogen and phosphorus removal effects. The treatment efficiency of this process generally reaches: BOD5 removal of more than 90%, COD removal of 70%–90%, total nitrogen removal of 70%–90%, and phosphorus removal of about 70%–90%.

The MBBR reactor (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor) is primarily used for the treatment of sewage and wastewater. It degrades and removes organic substances, ammonia nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen, and phosphorus from the water by forming a biofilm on the surface of the MBBR biological filler
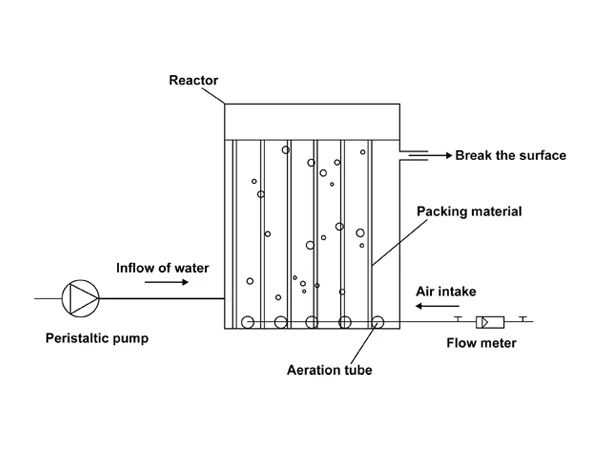
The MBBR reactor consists of a tank, carriers (fillers), and perforated aeration pipes.
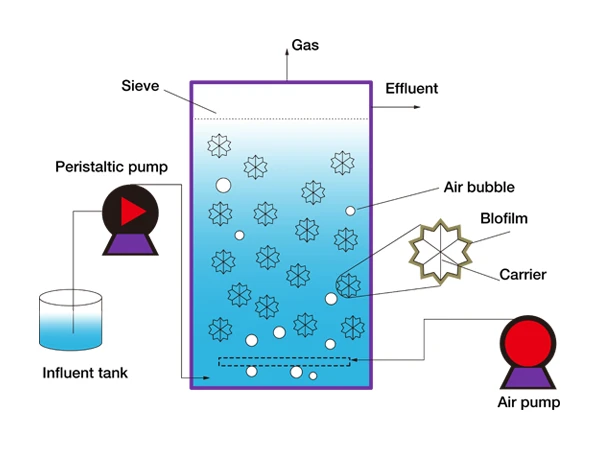
The principle of the MBBR process is to utilize the basic principle of the biofilm method by adding a certain amount of suspended carriers into the reactor to increase the biomass and biological species in the reactor, thereby improving the treatment efficiency of the reactor. Since the density of MBBR fillers is close to that of water, they are in a completely mixed state with water during aeration. The collision and shear action of the carriers in the water make the bubbles smaller, improving the utilization rate of oxygen. In addition, the biological species inside and outside each carrier are different. Some carriers have anaerobic or facultative bacteria growing inside, while aerobic bacteria grow outside. Each carrier acts as a micro-reactor, allowing nitrification and denitrification reactions to occur simultaneously, thereby improving treatment efficiency.
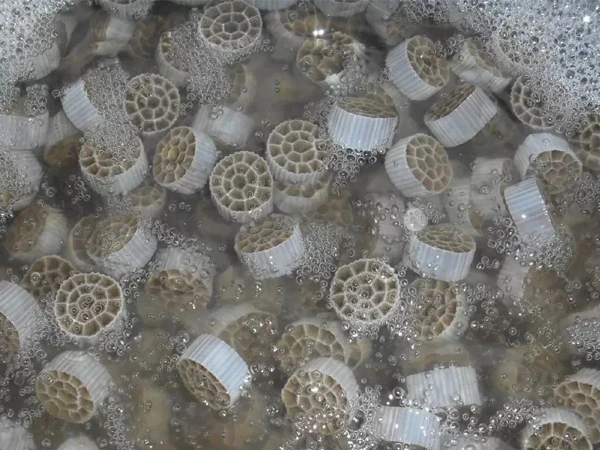

MBBR filler is a new type of bioactive carrier. It uses a scientific formula and integrates various trace elements that facilitate rapid microbial attachment and growth into polymer materials, based on the characteristics of the wastewater. It is modified and constructed through special processes, and has advantages such as large specific surface area, good hydrophilicity, high biological activity, rapid biofilm formation, good treatment effect, and long service life.
The core of the MBBR process is the carrier, whose physical structure, chemical stability, and mechanical strength directly affect the ease of biofilm formation, the speed of biofilm attachment, and the ability to remove pollutants. Generally, the carriers used in the MBBR process should meet the following characteristics:
Biofilm formation of biological fillers refers to the process in wastewater treatment where microorganisms attach pollutants in the water to the surface of the filler and grow and reproduce there. In an MBBR reactor, the biofilm formation process of biological fillers can be aerobic or anaerobic, depending on the contact between the filler surface and dissolved oxygen in the environment.
Aerobic biofilm formation. In the MBBR system, part of the filler surface is exposed to the air contact area, allowing oxygen to enter and support the microorganisms on the biofilm for aerobic respiration.
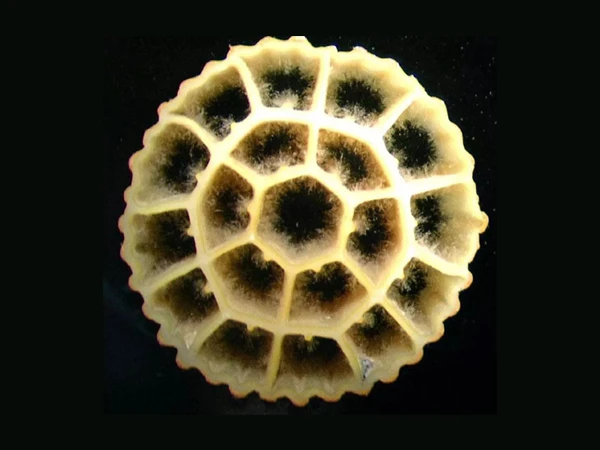
Anaerobic biofilm formation. In the parts of the filler that are in contact with water, microorganisms utilize the organic matter in the wastewater for anaerobic decomposition, producing metabolic products such as methane and hydrogen sulfide.

Anaerobic biofilm formation
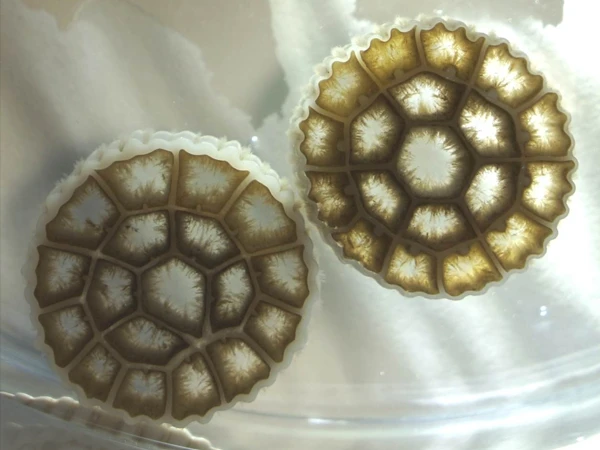

Aerobic Biofilm Formation
The biofilm is uniformly distributed on the surface of the carrier, becoming denser closer to the carrier surface and looser further away. The carrier's color darkens, indicating that the biofilm on the carrier has reached maturity.
The biofilm structure is dense and hosts a diverse range of microorganisms. Sessile ciliates, such as Vorticella and Epistylis, are predominant. The appearance of a small number of rotifers and swimming ciliates signifies the maturation of the biofilm.
There are many factors that affect whether biofilm formation can be rapid and effective, such as filler pores, pH value, temperature, and aeration rate.
The number of pores in MBBR fillers affects the efficiency of water treatment. The more pores there are, the larger the surface area of the filler, the more microorganisms can attach, and the better the treatment effect.
The physiological activities of microorganisms are closely related to the acidity and alkalinity of the environment. Only under suitable pH conditions can microorganisms carry out normal physiological activities. If the pH value deviates too much from the suitable range, the catalytic function of the enzyme system in microorganisms will weaken or even disappear. The optimal pH range for microorganisms involved in biological wastewater treatment is generally 6.5–8.5.
The MBBR method primarily achieves the degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater through the metabolism of various types of microorganisms in the biofilm. Therefore, the growth quality of the biofilm is directly related to the final outcome of wastewater treatment. This is especially true for nitrifying and denitrifying bacteria, which have long growth cycles and are very sensitive to environmental changes. The optimal temperature for nitrifying bacteria is 20 °C – 30 °C, and for denitrifying bacteria, it is 20 °C – 40 °C. When the temperature drops below 15 °C, the activity of both types of bacteria decreases, and at 5 °C, it completely stops. Thus, temperature changes will directly affect the growth of these bacteria.
If the aeration rate is too low, it is difficult to make the filler roll and fluidize; if the aeration rate is too high, it is difficult for the biofilm to form initially.
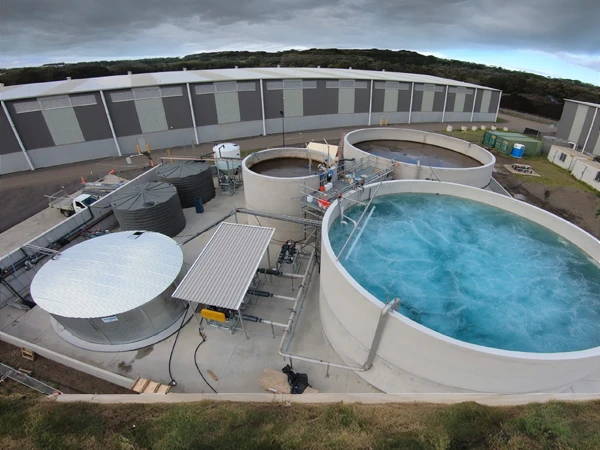
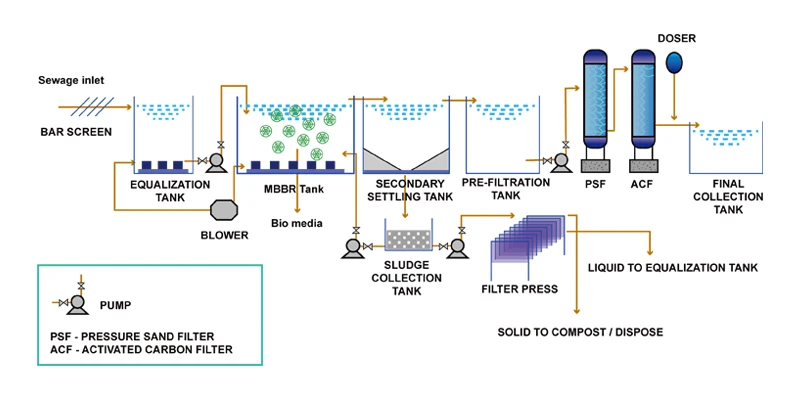
After the raw wastewater enters the wastewater treatment plant, it first passes through the screen equipment. The screen is composed of metal bars or rods arranged in parallel or inclined forms to block large particles and solid impurities, preventing clogging of subsequent treatment equipment. The water body treated by the screen enters the MBBR tank, which is filled with fillers. Microorganisms form biofilms on the surface of the fillers to degrade organic matter. The treated water flows from the MBBR tank to the secondary sedimentation tank, where suspended solids and biological sludge are separated by gravity sedimentation. The water exiting the secondary sedimentation tank enters the pre-filtration unit to further remove small particles and residual suspended solids that were not completely settled in the secondary sedimentation tank. The water that has undergone pre-filtration treatment enters the sand filter, which further removes suspended solids, colloidal substances, and microorganisms from the water. The water after the sand filter treatment enters the activated carbon filter, where the activated carbon's high adsorption capacity removes organic matter, residual chlorine, odors, and some heavy metal ions from the water. Finally, the water enters the clean water tank.
The biofilm reactor system should operate at temperatures of 15 °C – 35 °C.
Dissolved oxygen is an important factor affecting the removal efficiency of organic matter. Especially in cases where the goal is phosphorus and nitrogen removal, the control of dissolved oxygen concentration becomes particularly important. The control range of DO in each section of the reaction tank is as follows: anaerobic section below 0.2 mg/L, anoxic section between 0.2 mg/L and 0.5 mg/L, and aerobic section with dissolved oxygen concentration preferably not less than 2 mg/L.
The sludge concentration in the MBBR process should be controlled within 3,000 mg/L – 20,000 mg/L. Generally speaking, when the sludge concentration in the feed liquid increases, due to the high sludge concentration, sludge tends to deposit on the surface of the biofilm, forming a thick sludge layer. However, the sludge concentration in the feed liquid should not be too low, otherwise the degradation rate of pollutants will be low, and the ability of activated sludge to adsorb and degrade dissolved organic matter will weaken, resulting in an increase in the concentration of dissolved organic matter in the supernatant of the mixed liquor. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain an appropriate sludge concentration in the feed liquid, as both excessively high and low concentrations can reduce water flux.
The influent pH value of the MBBR reaction tank should be 6–9.
Advantages
The MBBR process retains the functions of the traditional activated sludge method while also incorporating the characteristics of the fixed-bed biofilm process. Its main advantages are reflected in the following aspects:
Disadvantages